💊 Intro to Pills
Pills are small draggable elements you can drop into a field of a form. There are different kinds of pills, including Variable, Function, Operand, Keywords, and Math pills.
Data Pills
Data Pills are dynamic variables used to represent key values in a form. Instead of hardcoding a form with a fixed number or string, you can use Data Pills to represent values that are not yet known but have a #. Meaning, you dont have to hard code values. For example, a pill that represents free balance, could contain different addresses at different times, depending on the data passed in from an upstream node.
Data Pills are what turn your Bagpipe scenarios into apps other people can use.
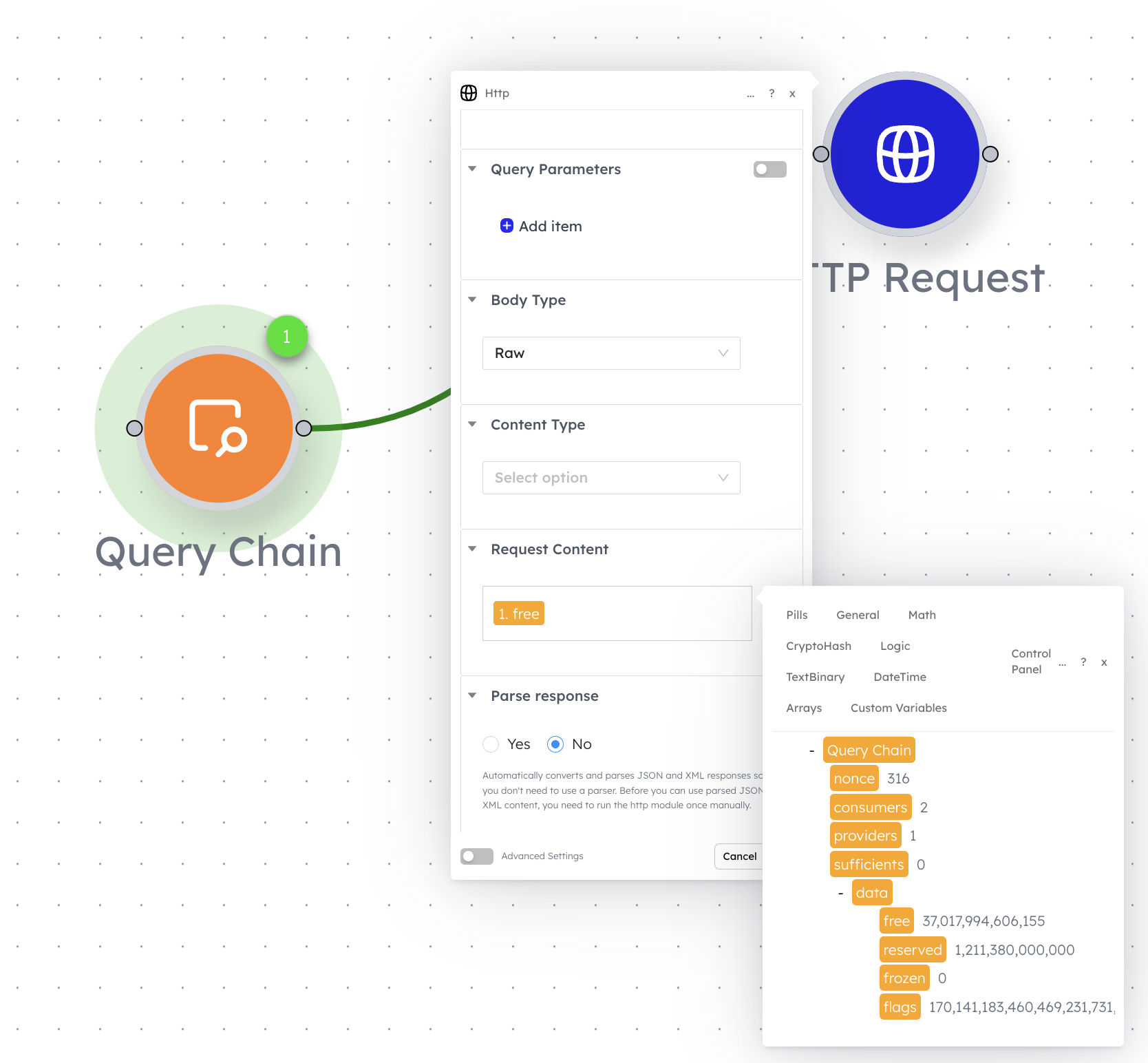
Above is an example of a data pill being added to a HTTP request field.
Function Pills
Function Pills allow you to add functions to a form field that take inputs and produce an output. There are several types of Function Pills, each tailored to specific operations:
Format Conversion Pills
Convert data from one format to another. For example, a stringToBytes() pill converts a string to bytes format at execution time.
Logical Function
These pills allow you to add logic such as if-else, switch statements, and more.
if-else: Evaluates a logical condition and returns one of two outputs. Example:if(a > b; 'a is greater'; 'b is greater or equal').switch: Returns the value based on the first true case from multiple options. Example:switch(a; 'A'; 'B'; 'C'; 'D').- etc.
Cryptographic Hash Function Pills
These pills perform cryptographic hashing functions:
sha256: Converts input data to a SHA-256 hash.ed25519: Uses Ed25519 algorithm for cryptographic operations.sr25519: Uses SR25519 algorithm for cryptographic operations.- etc.
DateTime Function Pills
Manipulate date and time values:
addSeconds: Adds a specified number of seconds to a date.addMinutes: Adds a specified number of minutes to a date.- etc.
Operands
Operands are symbolic representations that denote operations or processing steps within expressions:
=: Used for equality checks.!=: Used for inequality checks.AND: Logical AND operation, used to combine conditions.- etc.
Keywords
Keywords are predefined, reserved identifiers with special meanings, often used to simplify the logic of conditions or loops:
true: Represents the boolean value true.false: Represents the boolean value false.- etc.
Math
Math pills perform mathematical operations:
abs: Returns the absolute value of a number.ceil: Rounds a number up to the nearest integer.floor: Rounds a number down to the nearest integer.round: Rounds a number to the nearest integer.max: Returns the maximum value among the inputs.- etc.